Continuous Improvement
22 min read
Overcoming Manufacturing Lead Time | What Is Lead Time & How To Reduce It?

Manufacturing companies rely on their ability to get products to customers quickly and efficiently. If it’s one thing customers are not, it’s understanding when it comes to two factors: cost and speed of delivery.
Table of Contents
- What is Lead Time & Understanding Types of Lead Time
- Benefits of Reduced Lead Time in Manufacturing
- Factors Influencing Manufacturing Lead Time
- Calculating & Measuring Lead Time
- Identifying Bottlenecks & Delays
- Streamlining Production Processes
- Inventory Management
- Technology & Automation
- Final Thoughts
Customers want high-quality products delivered at a competitive price, and they want them now.
Manufacturing lead time is a measurement of the length of time it takes for a company to deliver a product to a customer, from when an order is placed to when the customer receives the finished product.
Several factors can affect a company's ability to deliver on the promise of fast order fulfillment and delivery.
Calculating lead time requires adding together all the steps in the process, including material procurement, processing, and delivery. That means that the supply chain, the production process, and shipping and delivery all come into play.
In 2021, the Institute for Supply Management released statistics showing the average time to receive production materials rose to 100 days – the longest window on record since the industry began tracking the figure in 1987.

Delays and uncertainties in the supply chain, arising from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, seriously strain manufacturers’ ability to keep lead times down. And the situation hasn’t eased much over the last two years.
Optimizing material replenishment, inventory management, and production processes can greatly affect a business’s ability to keep customers satisfied and loyal.
This article will explain how to calculate lead time, the benefits of shortening lead time, and exactly how to accomplish that goal.
What is Lead Time & Understanding Types of Lead Time
Manufacturing lead time is an overarching term that can encompass the entire length of time required to get a product to a customer.
However, there are several individual steps in that process.
Because of this, we can break lead time down into its components to better understand what lead time is and how the pieces come together to affect the outcome.
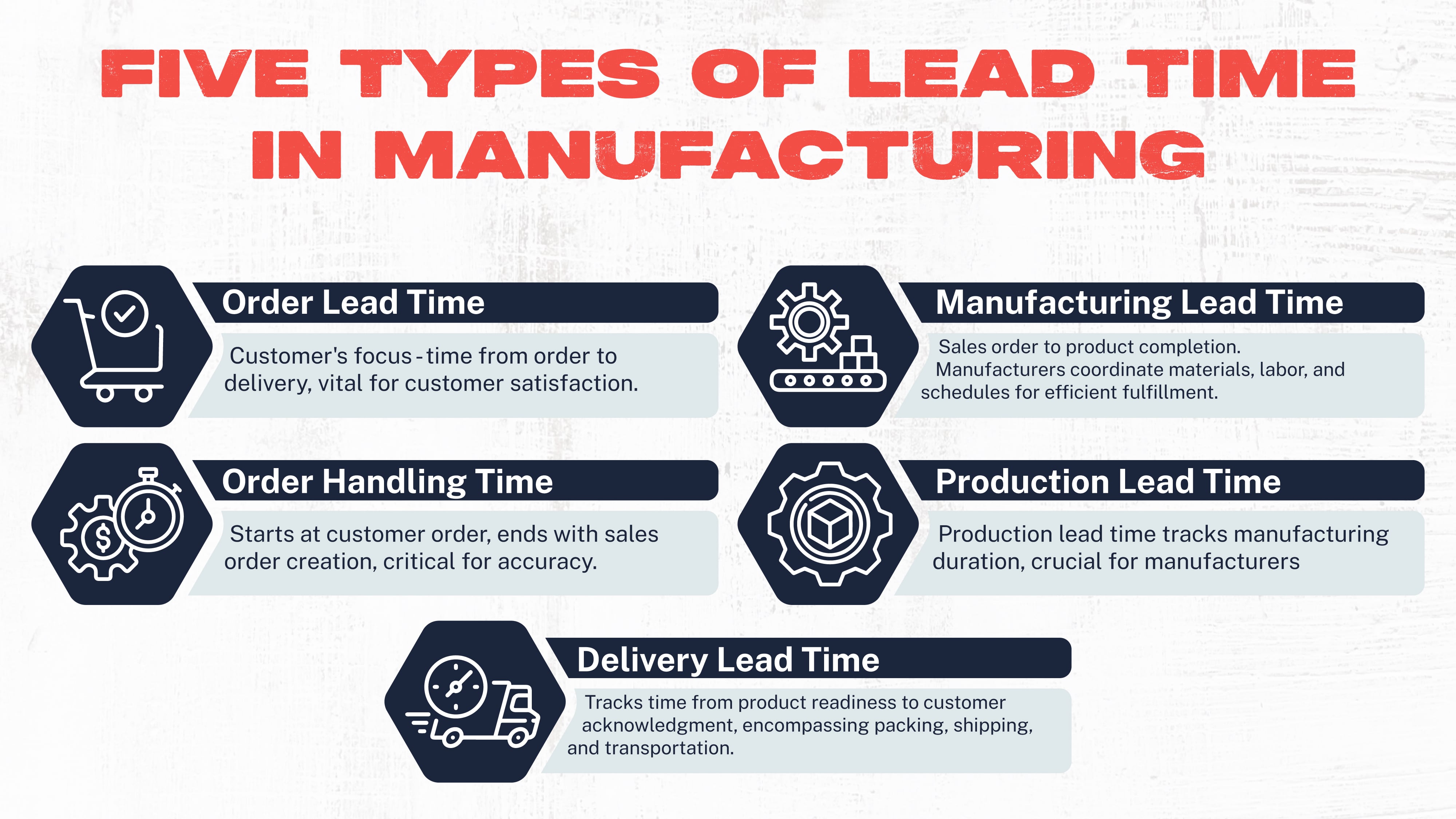
There are five different types of lead time involved in the manufacturing industry.
They are:
- Order Lead Time
Order lead time is defined as the time from when a manufacturer receives an order from a customer to when the order is delivered. Understanding order lead time can help organizations assess their ability to fulfill orders promptly and efficiently.
From the customer's perspective, this measurement is the most important and the only one they are truly aware of in the big picture.
The customer doesn’t care about delays in the supply chain or transportation disruptions. They only care about the length of time required for them to receive an order into their hands.
- Order Handling Time
The order handling time refers to the length of time from the moment a customer’s order is received until an actual sales order is created.
This process is vital to the transaction's success because errors along the way can mean customers don’t receive what they asked for.
This is the window where manufacturers must validate the order's details and the information required to process it correctly.
- Manufacturing Lead Time
Manufacturing lead time refers to the length of time from the creation of the sales order to the finalization of production or the moment when a product is finished and ready for delivery.
Once an order is entered into the ERP system, production can begin. Well, in theory, anyhow.
Manufacturers must first confirm the availability of required materials, schedule and plan labor and equipment use, and plan production schedules to meet order fulfillment promptly.
- Production Lead Time
Once an order is ready for production, another clock starts ticking. Production lead time is a measurement of how long a product spends in production, from when the first submodules hit production to when a final product is ready for delivery.
Production lead time is a vital factor for manufacturers and reflects the time and effort spent producing a finished product.
- Delivery Lead Time
Once a product is ready for delivery, organizations must track the time spent getting that product to a customer.
This is referred to as delivery lead time, including time spent on packing, shipping preparation, and transportation. Delivery lead time doesn’t end until the customer receives and acknowledges the delivery.
Benefits of Reduced Lead Time in Manufacturing
As with almost anything in life and business, time is money. It should be a given that getting a product to a customer quickly is beneficial for businesses.
But let’s get into the details of why organizations should be focusing on reducing manufacturing lead time.

Faster is Better
Whether discussing production, material procurement, order fulfillment, or delivery – faster is better. And when a company spends less time on each of these steps, they can be more productive overall.
The customers will certainly appreciate any effort to reduce wait times and speed up order fulfillment, if quality is not lost in the process.
A Resilient & Better Managed Supply Chain
Manufacturers rely on raw materials and supplies to build their products, and they need a fast and reliable way to get those materials. Reducing lead time requires a solid and transparent supply chain and reliable partners.
Focusing on these factors inevitably leads to greater accountability for all involved, improves a company’s ability to maintain and manage inventory levels, and builds a stronger business.
Reduced Waste & Lower Costs
Building a lean manufacturing environment is key to decreasing waste and costs while increasing productivity and efficiency. In part, reducing lead times can be achieved by eliminating unnecessary steps throughout the process.
What results is a more efficient and cost-effective production process. Saving time, labor, and resources is good for everyone.
Better Ability to Mitigate Risk
Reducing lead time, building a stronger supply chain, and optimizing inventory levels gives companies a better ability to minimize stockouts.
Optimized stock levels mean money saved on storage and more money earned from sales and revenue.
Delivery Accuracy Leads to Happier, More Loyal Customers
Optimizing shipping and delivery processes results in faster and more accurate delivery of products to customers. There’s nothing better for a company’s reputation than that. Shorter lead times mean more satisfied and loyal customers who will be willing to come back time and again for reorders.
Factors Influencing Manufacturing Lead Time
With so many individual steps coming together to form manufacturing lead time, it follows that there would be several factors that could negatively affect a company's ability to keep it short.
Below is a list of some of the most common factors affecting manufacturing lead time.
Material & Part Stockouts
Manufacturers cannot build products without the right parts and materials. An efficient production and delivery process will mean nothing if even one necessary component of a part is in short supply, or even unavailable.
Since material and parts stockouts inevitably result in longer lead times, ensuring that the right parts and materials are on hand when needed is essential. Building a reliable and resilient supply chain and vetting partners will help reduce the risk of costly stockouts.
Supply Chain Uncertainty
Manufacturers take a big risk when choosing supply partners because they are really at the mercy of those partners regarding lead times.
Every supplier is different, and that variability makes it difficult for manufacturers to predict when vital inventory stock items will be available accurately, and even harder to predict when they will arrive.
Shipping & Transportation Delays
One hard lesson learned from the global health pandemic is that parts and materials are only as good as the transportation industry’s ability to get them where they need to be.
With a crippling combination of raw material shortages, supply chain collapse, and a backlog of container ships sitting in ports for weeks, the industry took a hard hit.
And these unexpected circumstances are not limited to the effects of the pandemic. Natural disasters, human error, and even political landscapes can cause shipping delays.
Keeping Unnecessary Processes In-House
Many manufacturers looking to cut costs might consider keeping every step of production in-house rather than paying another invoice.
However, while outsourcing certain parts and processes might cost some dollars from the budget, it can also help reduce lead times.
Building every component of a finished assembly in-house adds to lead time and reduces the overall output from the production team.
Messy & Unorganized Inventory Control
And lastly, the bane of any business is inefficient and unorganized inventory management. It is essential to keep careful records of what is already on hand, when it will run out, and when those materials will be replenished.
Without careful control of these factors, companies will find themselves waiting for necessary parts before production can begin, not to mention wasting precious dollars on unnecessary materials and storage.
Calculating & Measuring Lead Time
Now it’s time to crunch the numbers. With so many individual components coming together to formulate manufacturing lead time, coming up with an actual figure might seem daunting.
Fortunately, breaking that equation down into its parts makes it easy to calculate. And it allows for a better understanding of how impactful each of those steps is on the final number.
Figuring out manufacturing lead time starts with carefully considering each step involved in the manufacturing process.
Listing each step, from material procurement, through production to delivery breaks the measurement into easily understandable chunks.
Take note of the time required for each step in the process for an accurate measurement. Then, plug those times into the equation below to calculate the total lead time.
The Lead Time Formula
For manufacturers, lead time combines manufacturing, procurement, and shipping time. For retailers, lead time is equal to procurement time plus shipping time.
For Manufacturers
Total Lead Time = Manufacturing Time + Procurement Time + Shipping Time
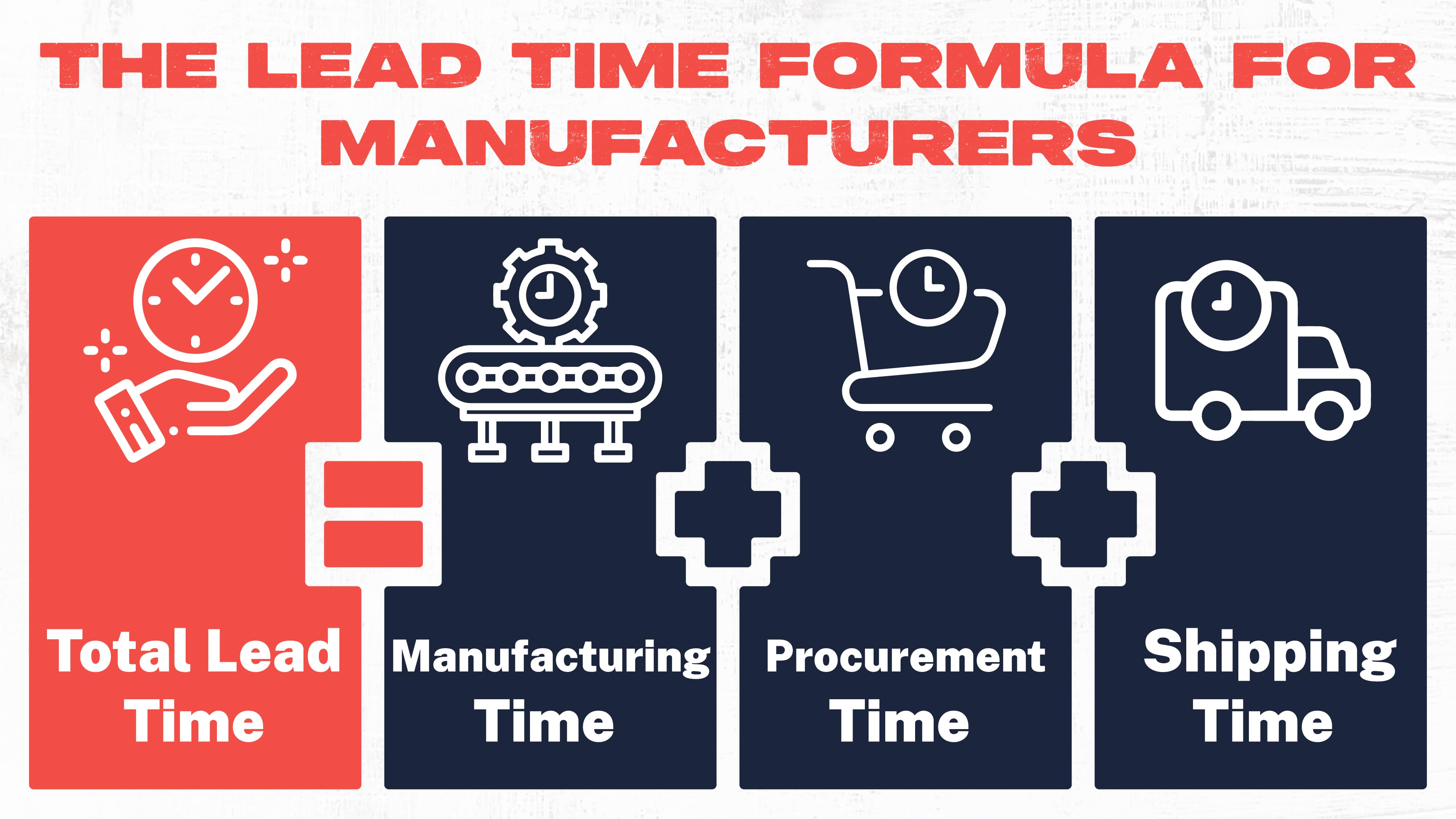
For Retailers
Total Lead Time = Procurement Time + Shipping Time
After determining the time required for each step in the process, all that’s left is to plug the numbers into the equation. Add the times together to determine the total lead time.
Identifying Bottlenecks & Delays
According to Manufacturing.net, almost 40% of industrial resources are wasted because of bottlenecks, resulting in a $12 trillion loss to the global economy.

That’s a big hit for manufacturers who are already fighting to maintain a competitive place in the market.
Preventing bottlenecks has incredible benefits for manufacturers, including increasing output and productivity, cutting costs, and reducing waste.
However, reducing bottlenecks' frequency also helps reduce manufacturing lead time. When production runs smoothly, teams can work on orders that need to be filled quickly and on time.
Here are some of the most common causes of bottlenecks in the manufacturing industry and tips on eliminating them.
Poorly Designed Processes and Workflows
Every manufacturer understands the importance of processes and the flow of those processes.
Trying to build success in the manufacturing industry without carefully planned and tested workflows is like baking a five-layer cake without a recipe. The results might be costly, unattractive, and potentially even inedible.
Poorly designed or outdated workflows, old and inefficient machinery, and even ineffective factory layouts can result in bottlenecks.
Manufacturers must revisit and reassess workflows regularly to ensure every step is as optimized as possible.
Labor Shortages
Production stops without proper labor power to get the actual work done.
Human resources are a vital component of any manufacturing company, and the lack of crucial personnel can certainly cause a bottleneck.
Efficiently filling production jobs is about more than propping up laborers in front of machinery.
Human resource management is responsible for keeping skilled, productive, and eager employees on hand to complete the work.
Overtaxing Equipment & Machinery
Every piece of machinery has a limit, and pushing these expensive and hard-to-maintain pieces of machinery past their capacity can lead to increased wear and tear.
And it can eventually lead to earlier-than-expected breakdowns and failures. Without the required machinery to fulfill production schedules, work comes to a stop.
A Lack of Automation & Technology
In today’s factories, technology, and automation play an ever-increasing role. The global industrial automation market is worth a staggering $190 billion, and that figure will only grow over the next decade.

There’s a reason so many manufacturers are turning to automation to streamline production and eliminate unnecessary human intervention in certain processes.
And that reason is because it works.
Implementing automation in the right places can eliminate the potential for bottlenecks, reduce inefficiencies, and protect against situations where labor shortages slow production.
Ineffective & Inaccurate Forecasting
Production planning relies heavily on forecasting. No matter the method used, manufacturers will find that poor forecasting results in unorganized and inefficient planning.
Poor and inaccurate forecasting can cause delays, wasteful waiting, and result in a revenue-stifling bottleneck.
Streamlining Production Processes
Manufacturers talk a lot about streamlining production – especially the suits and ties sitting around the boardroom.
That’s because streamlining production has a positive, trickle-down effect that can touch virtually every corner of the manufacturing industry.
And it certainly enables companies to reduce manufacturing lead times by empowering teams to be more efficient.
Such a broad topic can be difficult to define and even harder to achieve. But like most things in life, one must first start with the details to attain the bigger goals. Getting the little things right can have a huge impact on production.

Here’s some tips on how to get it done.
- Make Investments in the Right Places
A large portion of production relies on the efficiency and speed of the machinery used in the process. Investing in newer, faster, and more efficient machinery helps to streamline production in the most obvious way.
Better machinery usually results in a higher-quality product, fewer breakdowns and less costly maintenance.
- A Focus on Quality
Every component of a manufacturing company should include quality as a consideration. Customers demand it, and the market will reward companies consistently providing high-quality products.
Focusing on quality also results in shortened lead times because quality control reduces waste and lessens the chance of defective products coming off the line. Saving time, energy, and waste allows for a greater productivity and efficiency.
- Keeping it Organized
From a safe and clutter-free workplace to detailed maintenance and repair records, organization is key in manufacturing.
Companies must include intense organization and oversight to build the most efficient and streamlined workplace possible. Failure to do so can result in extended lead times and affect profitability.
- Build Better Communication
Effective communication is vital for any business, especially in manufacturing. Streamlining production requires giving team members the tools to be quick, safe, and efficient.
Technology has made communication, even directly on the plant floor, incredibly easy and accessible using communication software, radios, and wearable devices.
Switching from paper documents to digital storage has reduced the need for piles of paperwork but also made communication easier and more accurate.
Inventory Management
Manufacturing lead time relies on the supply chain's efficiency. That’s one reason manufacturing lead time and inventory management is two separate but closely intertwined topics.
Both influence the efficiency of the supply chain and affect a company’s ability to fulfill orders on time. Here’s how:
Lead Time & Forecasting Work in Tandem
The definition of Lead Time is the time spent between the start and successful completion of a project. This calculation helps companies in their efforts to estimate and forecast demand.
One informs the other, and they work in tandem to deliver fast customer delivery. A successful company uses lead time and market demand forecasts to determine what is required to replenish stock efficiently, fill orders, and meet demand.
Lead Time & Suppliers Work in Tandem
Understanding lead time and seeking to minimize it requires open and honest communication with supplier partners.
The same applies to inventory management. Companies must have a clear idea of when parts and materials will need replenishing, as well as the time required to get those materials.
Careful understanding and management of lead time and inventory are essential if manufacturers expect to optimize inventory levels. And the same is true for building a resilient and reliable supply chain.
Technology & Automation
A major advantage manufacturing companies have today is the incredible advancement in technology over the past several decades. Factory 4.0 initiatives have provided manufacturers with many automation and smart technology tools.
Manufacturers worldwide are busy transforming their factories in new and innovative ways, using technology that is helping them streamline processes, improve efficiency, and reduce manufacturing lead times.
Look at some ways technology is changing the industry and shortening lead times in the process.
- Automation
One of the most valuable tools manufacturers have now is the ability to automate production and procurement tasks. Automation helps build better processes and makes the entire supply chain work more efficiently and effectively.
- Streamlining Processes
Automation and technology also help streamline production and workflows by eliminating unnecessary and time-consuming tasks.
Consider the boost in productivity that team members can achieve when they’re not constrained by filling their workday with repetitive tasks.
- Communicating With Suppliers
Effective communication can help build a more robust and more responsive supply chain.
By understanding how lead times and forecasting demand work together and sharing that information with suppliers, the supply chain can better react and prepare for seasonal fluctuations or meet demand for large orders.
- Optimizing Inventory Management
Thanks to technology and automation, optimizing inventory levels has never been easier or faster.
Technology allows companies to automatically track and monitor inventory levels in real time, track inventory movement from the supplier to the customer, and set reorder trigger points.
All of this means companies have an improved ability to establish a secure and safe stock level, meaning customers are never left without the products they want. And companies aren't wasting precious money housing unnecessary inventory.
- Increased Visibility
Working together with technology is data. Better access to data, obtained through accurate collection and reporting methods in real-time, provides manufacturers with leverage they never had before.
Access to data helps companies make better, more informed decisions. And it gives them an increased ability to monitor, predict, and respond to problems that could negatively impact manufacturing lead times.
Final Thoughts
Lead time is critical for businesses that produce and deliver products to customers. Understanding manufacturing lead time is essential for companies seeking success in this industry.
It’s this careful understanding that allows manufacturers to minimize lead times. Because of the manufacturing process's complexity, from material procurement to the final delivery, the number of things that might go wrong is many.
The factors that affect lead time are also varied, and are often dependent on the type of product and the complexity of each process. The availability of raw materials, which is often an uncontrollable factor, also affects lead time.
The overall efficiency of the manufacturing facility itself even plays into the final equation.
And therein lies the challenge for manufacturers. Identify those factors that can add to increased lead times, pinpoint those areas where changes can do the opposite, and use those insights to build a better process.
Topic(s):
Continuous Improvement
Related Posts
View All Posts
Standard Work
How to Perform a Time Observation
5 min read
Without Standard Work, documented processes are often not used, or so out of date, that following them could become problematic. Standard Work is the foundation for any...
Continue Reading
Continuous Improvement
A Lesson in Lean Manufacturing From the North Pole
4 min read
If Santa Claus ran a toy company, he’d have the best lean manufacturing operations in the industry. A lean analysis shows that he delivers custom tailored products to every...
Continue Reading
Continuous Improvement
Book Club: "Leading Change"
10 min read
"Leading Change" by John Kotter offers an eight-step process for managing change and has become the foundation for organizations around the world. By outlining the process...
Continue Reading