Many manufacturers see reducing changeover time as a golden opportunity to improve operational efficiency and reduce waste. For good reason, a simple reduction in changeover time can increase output, reduce inventory/WIP, and improve responsiveness to customer demand.
Yet, the most effective method for standardizing and reducing changeover time is often overlooked — standardized work instructions.
The Benefits of Reducing Changeover Time
Say for example, that your current changeover takes an hour. Assuming you’re running 5-7 per week, that’s nearly one day a week spent running changeovers. At a minimum you could be wasting 32 days on changeover time per year.
Imagine what you could do if you got even half of that time back?
Those familiar with Lean manufacturing concepts know that changeover time is machine downtime, a non-value adding process (muda). Reducing changeover time not only has a direct time-savings benefit, but the flexibility of shorter changeover times allows for more nimble and reliable production cycles.
When it’s easier to switch between production runs, a higher variety of parts can be made and lead times become more predictable — meaning lower inventory, shorter production runs, and higher customer satisfaction.
What is Changeover Time?
Changeovers can mean a range of procedures depending on your production requirements, but the concept applies to all industries. Most commonly, changeover time is defined as the time elapsed from the last good part of the previous run, to the first good part of the following run.
The important part of the definition is the qualifier “good,” because a successful changeover is not complete until the new part run is meeting quality standards. After all, it’s not much value to do something fast if the end result is poor.
Changeover Time = the time elapsed from the last good part of the previous run, to the first good part of the following run
Changeover Time vs. Set-up Time
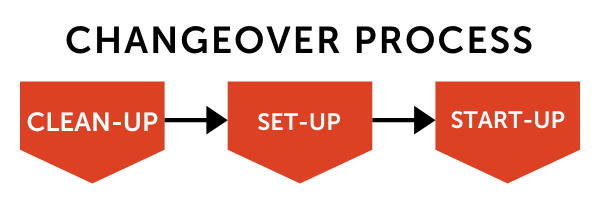
The two terms, ‘changeover time’ and ‘set-up time’ are frequently used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. Set-up time is simply a component of the changeover process. The entire changeover time also includes clean-up procedures for the previous run as well as start-up procedures for the next run.
SMED (Single Minute Die Exchange) and Standardized Work
Taiichi Ohno was famous for using standardized work to make monumental reductions in changeover times — sometimes by a factor of 20. With the help of Shingo Shigeo, they revolutionized how automotive manufacturing and other industries pushed themselves to become more efficient.
In conjunction with standardized work, Shingo Shigeo popularized the Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) method as two tactics to reduce changeover time. SMED, refers to a reduction in changeover time to less than 10 minutes.
SMED = a reduction in changeover time to less than 10 minutes
The basis of this methodology is to convert as many changeover steps to the “external,” or while the previous run is still active, and streamline/simplify the remaining steps as much as possible. “External” means outside of the current changeover procedure.
At its core, SMED is about standardizing and then improving. Standardizing your changeover procedures via work instructions is the most effective way to reduce changeover times and train new employees consistently.
How-to Create Standard Work Instructions
for Changeover Procedures
Before you improve any part of the changeover process, it’s best to get an audit of the current state. By using the standard work to document current best practices, you can create a baseline to measure efficiency gains and make improvements.
- BREAKDOWN: Start by breaking down the changeover procedure into its three main components: clean-up, set-up, and start-up.
- RECORD: Observe and document the process. Much like a time observation, be objective and record the work as clearly and concisely as possible.
Pro tip: Record a video of the process in addition to the in-person observation. Video can be helpful down the line when you need clarification on a step or help describing a particular technique. - DIVIDE INTO STEPS: Once you’ve specified the three main procedures of the changeover, break down each procedure into individual steps. Similarly, the SMED process begins by breaking down the procedures into individual elements. The best way to think about steps or elements is as individual actions. A typical changeover process can average about 30-50 steps/elements, but this can vary based on your production needs.
- TRACK CYCLE TIMES: Record the cycle time for each individual procedure, as well as the entire changeover process. This step is crucial to understanding the impact of your improvements. Remember, the timing begins at the last good part of the previous run and ends at the first good part of the next run.
- IMPROVE, DOCUMENT, REPEAT: Now that your process is documented and standardized, improvements can begin to take place. Start by considering which steps of the process can be moved to the "external" of changeover process. Then, brainstorm which steps can be streamlined and error-proofed (poka-yoke). As these improvements are made, make sure to document the process changes and communicate the updates to the workers on the floor.
The Benefits of EWI for Changeover Procedures
Electronic work instructions (EWI), such as Dozuki, are ideally suited to quickly document changeover procedures because they are more accessible, easy to use, and promote a continuous improvement culture.
Streamlined Process Improvement
Traditional methods for collaborating on standards via emails and Powerpoint files are disorganized and inefficient. Tools like Dozuki make it easy to author and revise documentation and automate approval processes before changes to the procedures are released to the floor.
Increased Accessibility![QR+Code+Gif+Dozuki]()
When changeover procedures exist only in paper binders, referencing and using the standards becomes a burden. EWIs can be used on tablets or smartphones; and with the addition of rugged cases, these devices can be used in just about any environment. Without the obstacle of binders, mobile tablets encourage your workers to utilize standards during changeover procedures and promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
Bonus: Using QR codes, operators can scan machines to instantly access the relevant setup procedures.
Standardized Document Control
Unlike their paper counterparts, electronic work instructions ensure that old standards aren’t floating around the production floor for operators to use. These give you confidence that operators are working from the current best practices for your changeover procedures.
Built-In Cycle Timing & Data Collection
Additionally, electronic work instructions allow you to ditch the stop watch and create more detailed time observation reports. Digital forms can capture data during the process to ensure standards are followed.
For longer changeovers, digital sign-offs can be inserted throughout the procedures to allow for quality checks along the way. Using this data, you can assess where bottlenecks in the process are and streamline, or move steps externally to the changeover.
Standardize, Improve, Repeat
Reducing changeover times is similar to other process improvement strategies - any PDCA methodology is built on standardization. Standard work instructions are the best method for not only reducing changeover times, but improving procedures across your operation.
Learn more about implementing standard work instructions with our free e-book.