Continuous Improvement
19 min read
How To Increase Productivity in Manufacturing

There are several ways to define productivity depending on the context. In terms of manufacturing, productivity relates to the speed at which quality work is performed. Increased productivity provides a greater return on investment and will lower your bottom line.
This leaves a larger percentage of profits available for growth and reinvestment.
Whether you’re thinking about starting a new product line or scaling your existing products, increased productivity can help generate the capital to make it possible.
Need a new building or a bigger fleet of vehicles? Increased productivity is how you can get there.
If the benefits are already available, why wouldn’t you take advantage of them?
In short, productivity is essential for success in manufacturing. If you're not focused on how to be more productive, you are leaving money on the table.
In this article, we will define and discuss the importance of productivity, how to identify and eliminate roadblocks, and how to increase productivity in manufacturing.
Benefits of Increasing Productivity in Manufacturing?
So, what is higher productivity worth to a manufacturer? Productivity in manufacturing relates to the output, or the product, which results from the combined inputs used to create that product.
It comes down to this: higher productivity means more products. More products equal more profit.
The processes used to increase productivity can result in the effective measurement of production in every department.
A company that doesn't ask itself how to increase production in manufacturing will suffer from backups in the production line, unhappy customers, and lower quality products.
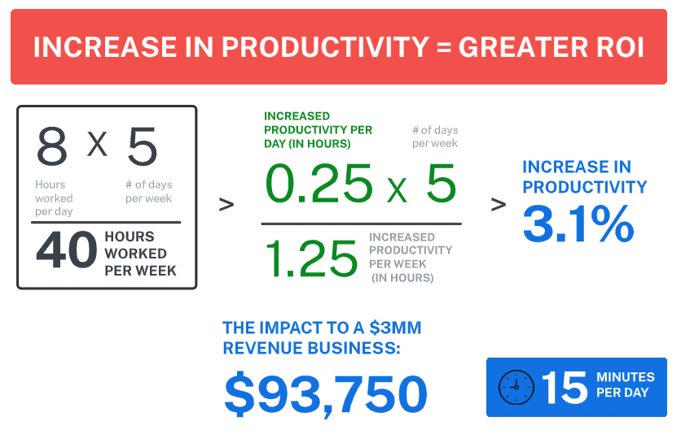
Greater ROI with Increased Productivity
Increased productivity aims to lower operating costs and increase the rate of production. This leads to a greater return on investments, which can then be reapplied for even more streamlined processes and practices, better technology, equipment, or even a greater labor budget.
Risk Reduction
Increased productivity results in greater oversight of processes on all levels and can lead to risk reduction in terms of machine or process breakdowns. A breakdown in production due to poorly maintained machinery will result in lowered product output and unhappy customers.
Information and Automation
Incorporating the use of data information for oversight of production issues will allow for greater insights. Technology that allows for the automation of repeated processes can increase productivity but will also have a significant impact on the overall competitiveness of a company.
Engaged and Successful Employees
Increasing the focus on operational employee and manager training, documentation, and self-assessment will boost productivity and create a more well-rounded, capable team. It also identifies employees with the potential and desire for promotion and greater responsibility.
Tools to Consider When Looking to Increase Productivity in Manufacturing
To increase productivity, it is necessary to identify the issues that may hinder it. One of the factors that must be addressed is workplace optimization, both on the physical level and regarding the workplace environment for employees.
Utilizing and optimizing every available space will naturally lead to a more productive workforce.
Things that can cause a disruption in productivity on the physical level include proper floor layout, bad lighting, air quality, or buildings and machinery in need of repair.
Regarding the health and wellness of employees, things like poor communication, unhealthy food options, and a lack of spaces designed for relaxation and camaraderie can all affect productivity.
Unengaged employees who are stressed or in poor health can eventually suffer burnout, resulting in higher turnover for a company.
So, what are some tools available to increase productivity in manufacturing by solving the problems related to the workspace?
Automated Systems
Implementing automation in the right areas will free-up employees for other tasks. Automation can simplify processes like ordering materials, billing, report generation, and inventory management.
The Right Equipment
Choose the right machinery and technology for the biggest benefit. Adhere to maintenance schedules and repair processes to limit downtime caused by breakdowns.
ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning software offers many benefits to help streamline processes and provides valuable insights based on real-time analytics.
Data Tracking
Implementation of data tracking to identify and assess problem areas can save time and energy spent on troubleshooting and guesswork.
Workforce Management Applications
Using a workforce management application offers customizable tools for the tracking of tasks and projects and allows for communication between employees and managers in response to specific goals.
Email Managers
Using an application to allow for open communication between members of the supply chain can help to address problems quickly and effectively.
Developing a System to Improve Manufacturing Process
What are the steps a company can take to improve its processes and gain productivity?
Developing a structured system that can identify problems and provide oversight where necessary will benefit everyone involved.
Here are some steps to take to develop a system that answers the question of how to increase productivity in manufacturing.
Ask Your Team
Get opinions from employees and managers, as they’re the ones who do the work every day and can offer valuable insights into shortcomings and potential areas of improvement.
Ask The Right Questions
Break down each step of the process, from the beginning to the final product, and seek to identify where improvements can be made. What are the repeated processes that need to be in place at each level of production to streamline productivity and prevent slowdowns?
Assess The Workforce
Make sure your staff is properly trained, including onboarding and off-boarding, to prevent any issues related to expectations and compliance. Are employees in the right place in the process for optimization of their skills?
Assess The Technology
Are the machines, tools, and technology optimized for performance? Is there a way to make improvements or add value with advancements?
Use Models
Model-Driven Development uses information and inputs and measures their resulting outputs. Using digital models allows for troubleshooting and experimentation with each step in the process without jeopardizing production.
Look At The Big Picture
Put all the pieces of the puzzle together. Ask and answer questions about how implementing changes will affect the process, the employees, and the company.
Understanding Why Efficiency in Productivity Matters in Manufacturing
Improving productivity is important for manufacturers, but that increase won’t be as valuable without the added component of efficiency. And though the two are related, they are not the same.
Streamlining processes to create more output at a faster pace results in an increase in productivity. But efficiency means that every step of that process is optimized to produce a more valuable product, based both on quality and cost.
Ensuring efficiency is present in your manufacturing process will lead to a greater return on investment than productivity would on its own.
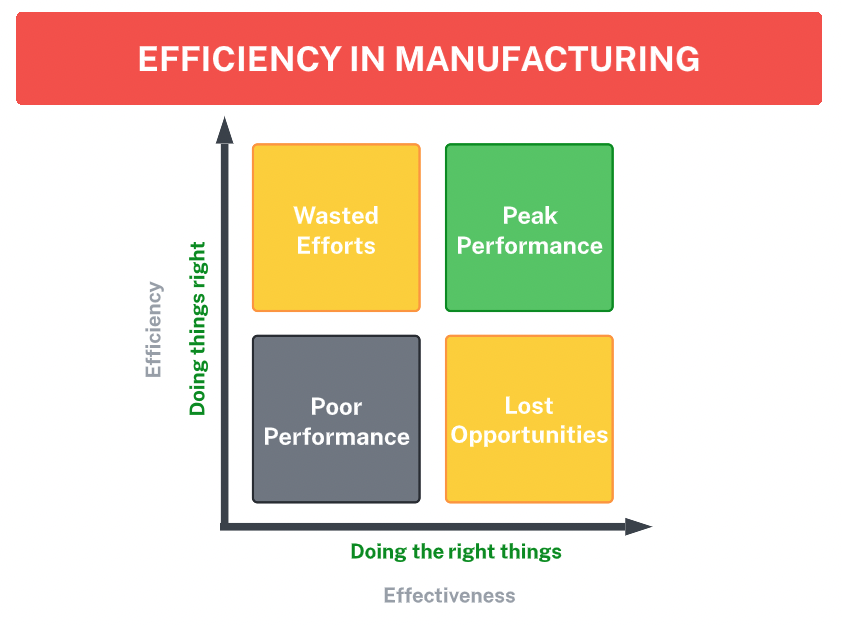
Efficiency can be expressed as a calculation of standard output divided by actual output. Productivity is a measure of how efficient the processes are.
Efficiency has a broader definition and includes information about individual processes and optimization. It works to guarantee optimal use of every component, without waste or risk and ensures the quality of products produced, not just the quantity.
Increased efficiency can be applied to create a lean manufacturing process, meaning the use of raw materials and resources are optimized in order to lower cost per unit and reduce costly waste.
There are software programs that can help calculate efficiency based on a series of inputs, like the cost of materials. You can also invest in software that will monitor machinery used in production to give insights into performance in real-time.
Comparing Labor Productivity and Employee Productivity
One of the biggest components of any company is its employees.
The people who perform the actual work of manufacturing a product could not be more important to the overall result of that product, both in the quality of work they perform and the cost of paying them to perform that work.
When considering how to increase productivity in manufacturing, one must investigate the cost and productivity of the workforce. But there is a difference between labor productivity and employee productivity.
Employee productivity can be expressed as an equation that divides the value of an input by the cost of a unit of labor.
In simpler terms, it’s how much value an employee produces in exchange for one hour of work. Measure, track, and document every employee’s efficiency and productivity over time.
However, employee productivity is an individual measurement that differs for every employee and can change over time based on individual circumstances.
Labor Productivity can be explained as the communal measurement of the entire labor force in a department or even the entire company. This equation is similar, measuring the value of goods produced against the cost of labor required to produce those goods.
Labor productivity involves a bigger scale and encompasses the entire workforce.
Both measurements are important to increasing and maintaining productivity. The difference is that managers address employee productivity on an individual basis, using management, oversight, and training techniques designed to boost the output of a single employee.
Managing and increasing labor productivity will have a larger and more noticeable effect on overall manufacturing productivity, and so requires greater urgency.
Manufacturing Waste – The Elephant in the Room
Production of almost any product creates a waste of some kind, and logically this practice would lead to higher overhead costs and decreased profitability.
Recent environmental regulations have led to an even greater need for companies to actively develop a lean manufacturing process that seeks to limit or even eliminate waste.
There are numerous ways that companies wind up with waste from their manufacturing processes.
Defective products result in waste, but overproduction, mismanaged inventory and ordering controls, or lack of coordination in the transportation of goods can all lead to waste.
Manufacturers who use perishable or damageable materials are at a higher risk for problems.
The type of waste produced by manufacturers can vary greatly, and so the solutions for how to repurpose or shrink the amount of this waste must differ as well. Common types of material waste are solid waste, chemical waste, and toxic waste.
Solid waste and chemical waste mostly refer to raw materials leftover or unused after manufacturing.
Toxic waste is usually a byproduct of the production process and must be carefully handled to avoid contamination and guarantee adherence to environmental compliance procedures.
Other kinds of waste are less physical material and more of a waste of resources and capital.
Waste can also be things like time lost due to lags in production lines, or damage to materials, and equipment from external sources. Even waste produced by mistakes or over-processing resulting from miscommunication can eat away at profits.
Improving Productivity by Actively Reducing Manufacturing Waste
The proper management and reduction of waste materials will help to increase productivity in manufacturing and protect your bottom line.
Implementing safety measures and oversight procedures will help to build a lean manufacturing process and reduce the amount of waste created, as well as effectively repurpose materials that can be reused or recycled.
Preventative measures should be a frontline defense in reducing waste created by manufacturing, and these preventative measures include:
Inventory Control
Efficiency in the inventory control process is number one and will ensure the number of materials on hand matches the need for production.
Maintenance Schedules
Ensuring that machinery gets the proper preventative and scheduled maintenance will limit the amount of time a machine is down, which could lead to waste materials that can’t be utilized before decay occurs.
Organization
Another oversight technique that will help reduce waste is as simple as staying organized. Proper rotation and labeling of incoming and outgoing raw materials, efficient handling of damaged products, and basic organization will eliminate errors and oversights in inventory handling.
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Consider materials consumed regularly in the packaging and shipping department that can be altered or repurposed to reduce waste. Recycle raw materials that can’t be repurposed whenever possible.
Audits
Regular audits and documentation of machinery conditions, processes, inventory, and warehouse conditions is one way to catch potential problems before they occur and identify ways to improve waste production.
Training
Training is everything in business, and properly educated employees will help to lower waste created by mistakes.
Documentation
To ensure compliance with government regulations and the EPA, proper documentation of waste disposal practices is vital. Improper records may result in costly fines and other penalties.
Operational Efficiency Playing a Role in Increasing Productivity Level
If companies want to know how to increase productivity in manufacturing, they need to step back and look at the big picture.
Operational efficiency refers to the overall efficiency of operations in a company, including processes, activities, labor management, risk reduction, quality control, and more.
It's the sum of the parts that make up the operations of a company.
Maintaining efficiency across the operations of a company will lead to an increase in productivity by identifying areas that may be problematic and recognizing processes that are ripe for improvements.
A more efficient operation leads to a higher quality product by way of streamlined processes, active oversight in needed areas, and a more productive workforce.
The best way to increase operational efficiency is similar to the ways to increase productivity because the two concepts are connected. It’s hard to have one without the other.
Measuring operational efficiency should be a priority component of any manufacturing endeavor, and involves tracking measurable data like input, output, and performance indicators.
Increasing automation is a popular avenue for companies in the new age of data science and technology, and allows for the freeing of labor and resources toward other expenditures.
Machine learning and model development for testing processes and providing valuable insights have never been more available to companies of all sizes.
Training employees properly is invaluable to operational efficiency.
Waste reduction techniques, proper floor layout, inventory management, and safety protocols all contribute to increasing efficiency across departments, which will lead to increased productivity.
Final Thoughts
For any company, business, or industry, many puzzle pieces need to be carefully fitted together to get a full picture. Little pieces fit together to form big pieces, which combine to create a finished product.
Without the proper procedures, protocols, and systems, companies will struggle to maximize productivity and efficiency.
The point of business is profit. And while other benefits may come along the way, such as personal fulfillment, the success and happiness of employees, and even a positive impact on the economy, none of that would be possible without the profit generated from the business.
Companies in the manufacturing industry must always keep an eye on ways to increase productivity to maximize efforts toward a higher return on investment. With the right processes and systems in place, the sky’s the limit.
Related Posts
View All Posts
Standard Work
11 Common Manufacturing Challenges & Solutions | 2023
25 min read
When it comes to industry, manufacturing might be one of the most challenging. Because of the high cost of doing business, the need for skilled workers, and an...
Continue Reading
Standard Work
5 Ways To Improve Quality Control in Manufacturing
22 min read
In manufacturing, quality is everything. Businesses need to focus on creating products that are high quality enough to meet or exceed the customer's needs if they want to be...
Continue Reading
Continuous Improvement
The Most Common Manufacturing KPIs and Metrics to Track & Why | 2023
19 min read
Manufacturing is a highly competitive industry, and the road to success has been uphill for many businesses over the last several years. Table of Contents Criteria for...
Continue Reading